13 Residential Construction Technology Trends to Watch in the Coming Years

In the past few years, I’ve seen residential construction change faster than at any other time in my career. The pace of new project management tools and methods entering the field is no longer gradual. It’s constant, and it’s reshaping how homes are designed, built, and managed.
What stands out to me is how residential construction technology trends solve the long-standing problems that used to hold projects back. Delays, cost overruns, and inefficiency have always been part of construction.
Now, I see more builders turning to advanced materials, automated methods, and digital platforms to keep construction cost tracking predictable and timelines steady.
The shift reflects a focus on practical solutions that actually change how homes get built. Therefore, I’ll be sharing the 13 most impactful residential construction technology trends we have already witnessed and expect to see growing, and making our industry expand.
Table of Contents
- Current Industry Statistics
- Innovative Building Materials
- Modern Construction Methods
- Digital Transformation in Construction

Current Industry Statistics
Residential construction is expected to account for a growing share of tech adoption. According to a 2024 Statista survey, nearly 41% of mid-sized U.S. homebuilders reported adopting at least one advanced digital tool in their projects, a sharp rise compared to 32% the year before.
That number is only going up. I believe that the firms that adapt early will have a clear advantage in efficiency, sustainability, and client trust.
Innovative Building Materials
New materials are shaping how homes perform, both during construction and long after. Stronger composites, energy-efficient products, and smarter insulation methods are now standard discussion points on projects. I’ve noticed that when these materials are applied consistently, they not only cut operating costs for homeowners but also help builders deliver projects with fewer callbacks and warranty claims.
Recent market data backs this up. A 2025 Allied Market Research report shows that the global advanced building materials market is projected to reach $111.7 billion by 2031, growing at over 6.8% annually, with residential projects being one of the top drivers. Such growth tells me that these materials are not niche anymore as they are entering mainstream housing.
1. Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT)
I’ve worked on projects where cross-laminated timber (CLT) replaced traditional framing, and the difference in speed was obvious. Large prefabricated panels go up quickly, reducing labor demands and cutting down waste.
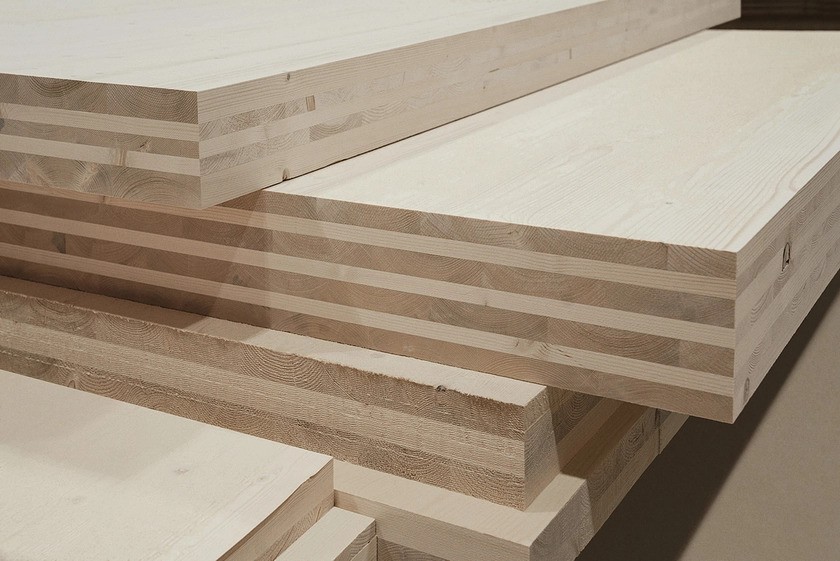

CLT is also making waves because of its sustainability profile. According to a study, using CLT can lower a building’s carbon footprint by up to 26.5% compared to concrete or steel framing.
The rapid adoption makes it especially attractive for environmentally conscious clients.
2. Insulated Concrete Forms (ICFs)
ICFs are not new, but I’ve noticed their use in residential builds increasing over the past two years. These interlocking blocks create insulated walls that outperform traditional wood framing in energy efficiency. Homeowners notice the savings in utility bills, and builders appreciate the durability against extreme weather.
3. Smart Glass and Advanced Insulation Materials
Smart glass is no longer limited to high-end commercial buildings. It can be specified for residential projects, especially in energy-conscious urban developments. Smart glass construction technology automatically adjusts transparency to regulate light and temperature, lowering HVAC loads.

Pair that with advanced insulation foams and phase-change materials, and the home performs at an entirely different level. According to DOE 2024 data, smart glass installations can cut annual residential cooling loads by 25-30%. That’s a measurable impact for both owners and builders.
4. Self-Healing Concrete
This technology is still progressing, but I’ve followed pilot projects closely. Self-healing concrete uses embedded bacteria or microcapsules to automatically seal small cracks when exposed to water.
In residential foundations and driveways, this could dramatically extend service life. Early field tests even report that the maintenance costs may be cut significantly thanks to self-healing concrete, resulting in stronger buildings over a 20-year period. For builders, this means fewer callbacks and warranty claims.
Modern Construction Methods
Alongside new materials, I’ve watched construction methods shift just as quickly. The pressure to build faster, cheaper, and greener is forcing builders to rethink how homes come together. Traditional stick framing is still common, but newer methods are gaining ground because they solve persistent problems from labor shortages to energy use.
Industry adoption is accelerating. The growth we see now matches what I’ve seen on the ground: when projects adopt these methods, the learning curve is real, but the gains in speed and efficiency are hard to ignore.
5. 3D Volumetric Construction
3D-printed components move from small demo projects to actual housing starts. Volumetric construction of entire rooms or modules built off-site is speeding up delivery times. A 2024 survey in Europe reported that using volumetric methods can cut build schedules by 20-50%, depending on project size.
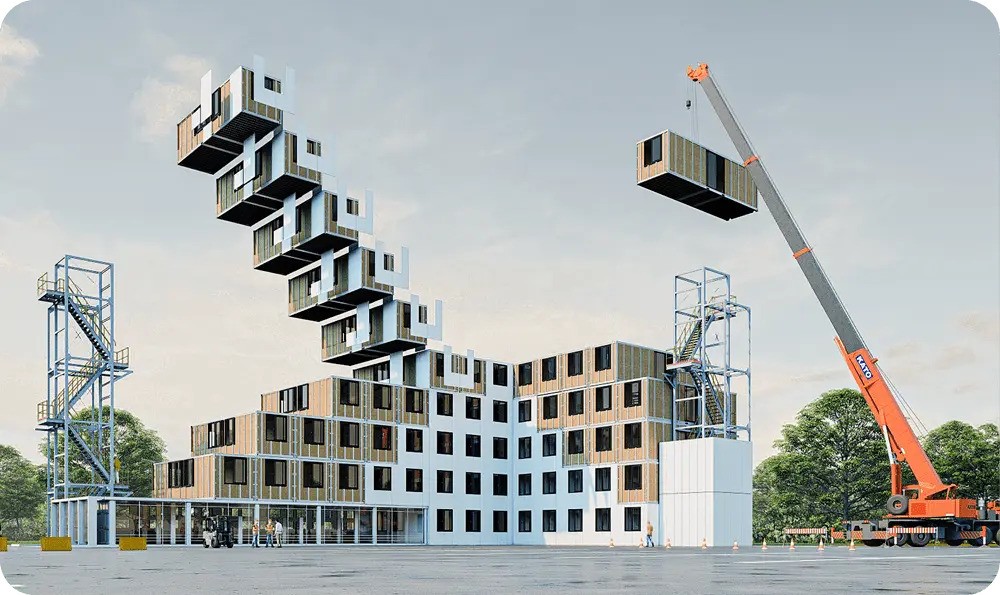

As a result, for residential builders facing tight labor markets, this approach is becoming a serious option, not just an experiment.
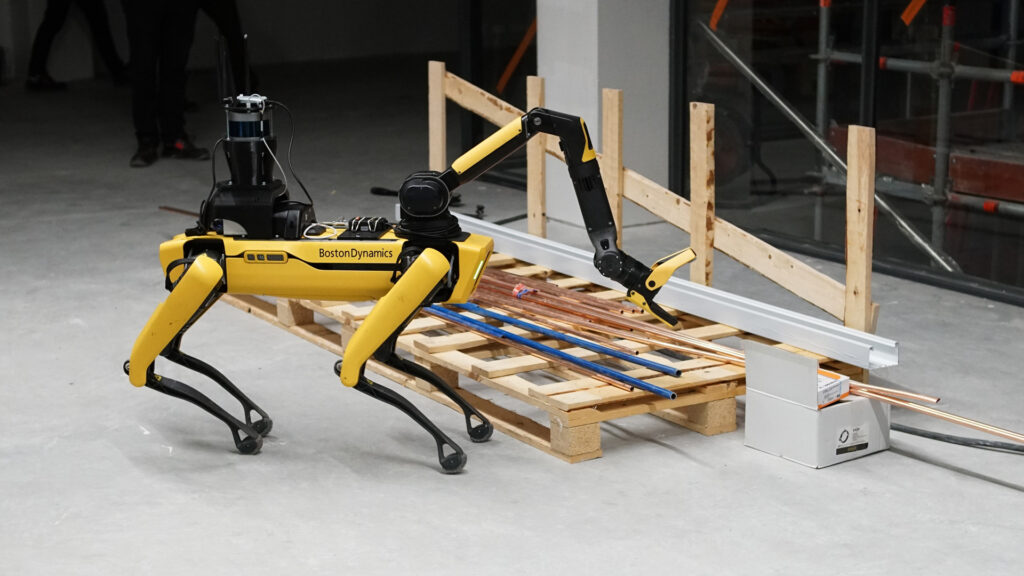
6. Robotics and Automated Machinery
Robots are no longer science fiction on construction sites. We now have brick-laying robots and rebar-tying machines in action. They don’t replace the crew but handle repetitive, labor-heavy tasks, letting skilled workers focus on detail work.
According to a 2025 Deloitte report, contractors using smart manufacturing methods reported labor productivity gains of up to 20%. For smaller firms, the entry cost is still high, but adoption is spreading as rental options and service providers grow.

7. Green Roof and Passive House Construction Techniques
Sustainability is not just a selling point anymore, as it becomes a standard regulation in most regions. I’ve been involved in projects where Passive House standards cut energy demand to a fraction of typical builds. Green roofs, while more common in urban areas, are being tested in suburban housing as well.
A 2024 Passive House Institute study showed homes built to the standard used up to 80% less heating and cooling energy. The residential construction technology is not just good for the environment, as it also locks in long-term affordability for owners.
8. Drones in Residential Construction
Drones are quickly moving from “nice to have” to everyday tools. Site superintendents use them to document progress, verify deliveries, and even assist in roof inspections. This cuts down the need for multiple site visits and reduces safety risks.
For us, the biggest gain has been in progress reporting, while clients appreciate visual updates that show exactly where the project stands.
Digital Transformation in Construction
From my perspective, digital tools are no longer optional. I’ve watched residential builders struggle with delays, miscommunication, and paperwork, only to adopt digital systems later and see immediate improvements. The shift is removing delays that used to cost weeks and thousands of dollars.
Data backs this up. A 2025 Dodge Construction Network survey found that builders using integrated digital platforms have better decision-making processes, growing by 66%. That reflects what I’ve seen myself: once communication moves to real-time platforms, the excuses about “I didn’t see the update” disappear.
9. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Residential Construction
AI has moved from hype to actual job site applications. Today, AI tools analyze schedules, flag risks, and even predict which subcontractors are likely to miss deadlines.
According to a recent PwC report, AI-driven project management systems improved forecasting accuracy by nearly 25%. In residential construction, that means tighter cost control and fewer surprises for both builders and homeowners.
10. Digital Twins in Residential Construction
Digital twins once felt like something only mega-projects would use. But they can also be applied in housing developments, creating virtual replicas of homes before they’re built. This lets teams test different designs, materials, and even energy-use scenarios before construction starts.
Digital twins also support ongoing facility management after construction is complete. Homeowners and developers can use the model to monitor system performance, predict maintenance needs, and track energy efficiency in real time. This residential construction technology creates a feedback loop where lessons learned from completed projects can be applied directly to future designs.
11. Augmented Reality (AR) in Construction
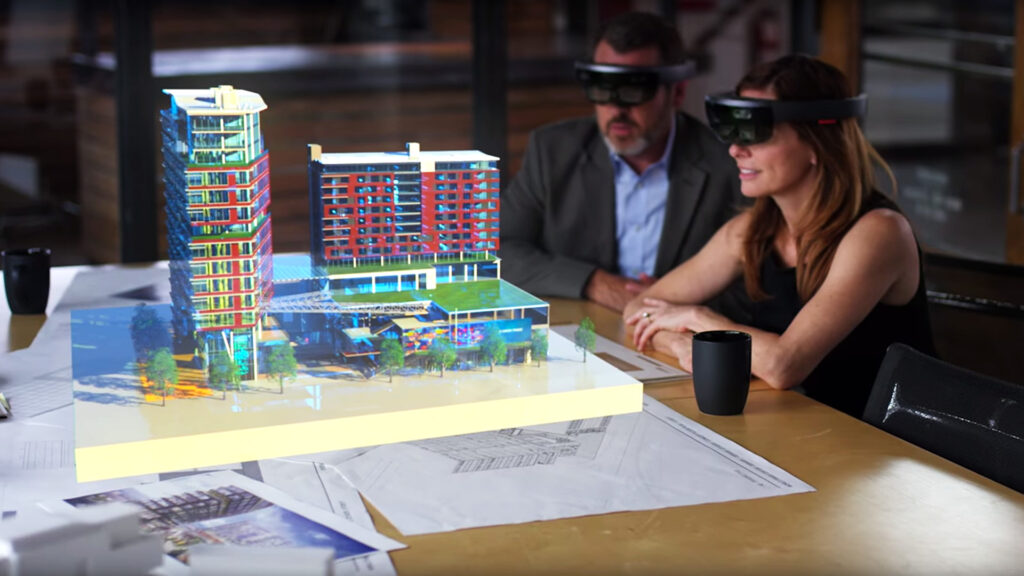

AR has started showing up on job sites more often than you think. Our team used AR to overlay plumbing and electrical layouts on walls before drywall went up. It immediately showed where conflicts would happen. In one project, this saved days of rework by catching errors early.
Beyond clash detection, AR also helps improve communication with clients and inspectors. Being able to walk through a space and see design elements in place makes approvals faster and reduces misunderstandings.
12. Cloud-Based Project Management Software
My team relies on cloud-based construction systems to bring everyone involved in the project together. Instead of field supervisors sending updates by text, everything goes into one shared platform.
Moreover, office staff, subcontractors, and even clients can see the same data. It reduces endless back-and-forth and keeps team messaging and accountability clear.
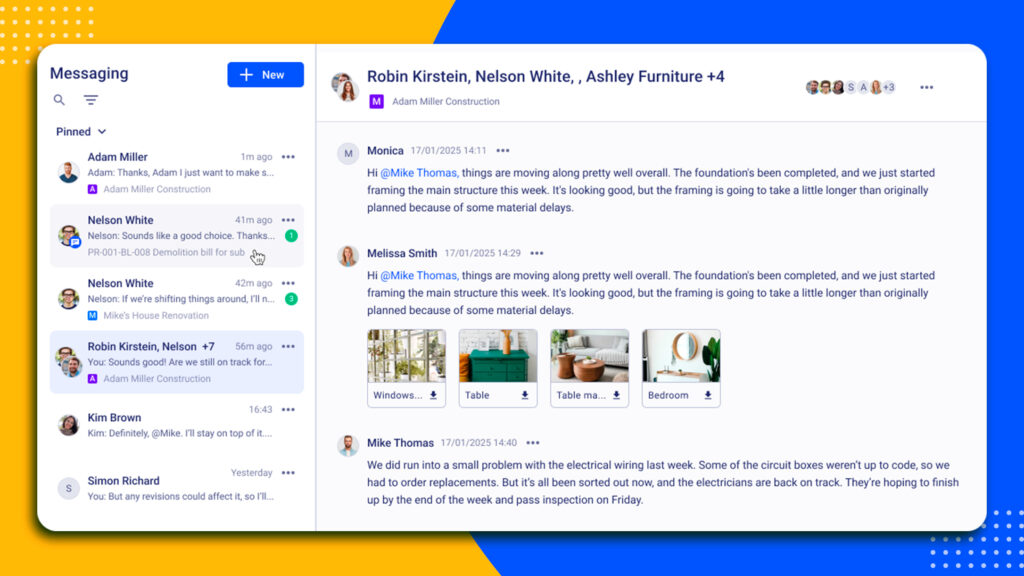
Cloud-based platforms also create a single source of truth for all project data. Drawings, RFIs, change orders, and schedules are updated in real time, so there’s no confusion about which version is current. Specialized software helps subcontractors plan their work more accurately, while office teams can track budgets and commitments without waiting for paper trails.
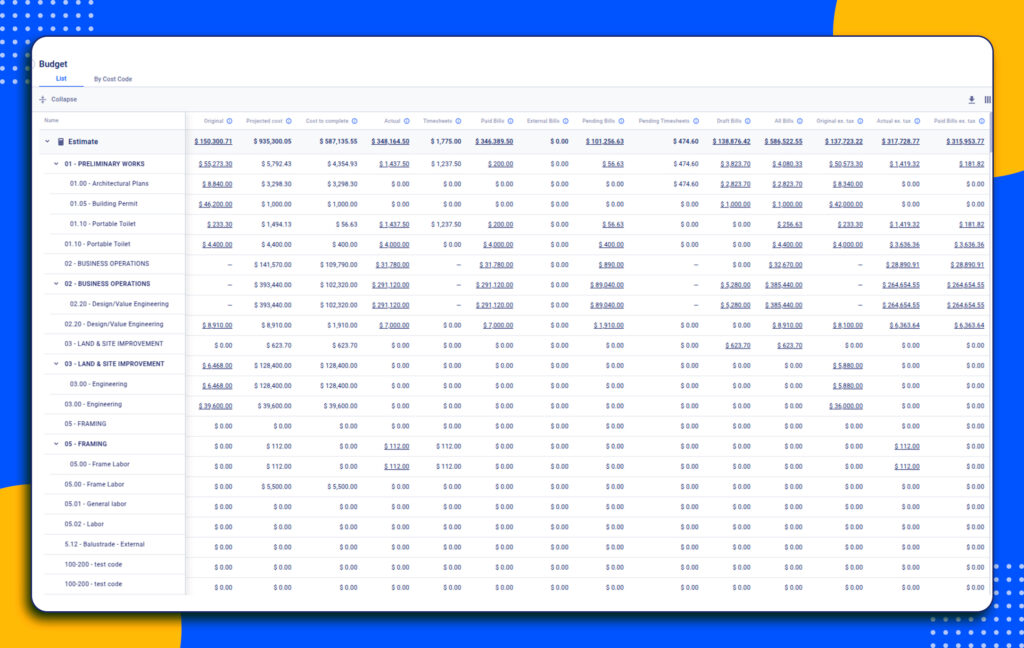
Over time, it builds a documented history of every decision made on the job, which is invaluable when disputes or warranty issues arise.
13. Building Information Modeling (BIM) for Residential Projects
For years, BIM was viewed as a tool mainly for commercial buildings. That’s changing fast. I’ve worked on residential projects where BIM streamlined coordination between architects, engineers, and builders. It makes the design more transparent, reduces clashes, and gives owners a clearer view of what they’ll get.
The Bottom Thoughts
Looking back at these 13 trends, a few ideas stand out clearly:
- I’ve seen innovative materials like CLT and ICFs improve both performance and sustainability in residential projects.
- New construction methods, from 3D volumetric to robotics, are shortening build times and addressing labor challenges.
- Digital tools, especially AI, AR, and BIM, are changing how teams communicate and avoid costly rework.
- Cloud-based systems and dashboards are keeping field and office teams aligned in real time.
- Builders who adopt these technologies early position themselves for stronger client trust and better long-term margins.

What Is Residential Construction Technology?
From my own work and research, I define residential construction technology as every material, method, and digital tool that improves how homes are built. This includes advanced building materials like CLT, modern methods such as modular and 3D construction, and software platforms that connect the field with the office. It’s not limited to one category, but includes a combination that drives better cost predictability, faster delivery, and more sustainable housing.
How Is AI Being Applied in Homebuilding Projects?
On the project management side, AI tools forecast risks, highlight schedule conflicts, and improve cost predictions. On the design side, AI helps analyze multiple layout options and material choices in seconds. In residential projects, I’ve used AI-enabled systems to flag potential delays in subcontractor work before they became major problems. The result is tighter control over timelines and budgets.
What Are the Latest Construction Technologies?
The list grows every year, but a few stand out. In materials, CLT, ICFs, and self-healing concrete are gaining traction. In methods, robotics, drones, and modular builds are pushing speed and consistency. AI, AR, BIM, and cloud project management are also becoming standard tools on residential sites. I’ve noticed that the most successful builders are the ones blending these areas rather than relying on a single innovation.


